Is the molecule in organisms that carries the biological instructions that make each one of us unique.
It affects many of our characteristics, such as our physical, emotional and behavioural features. The information stored in DNA is passed down from generation to generation. As a result, genetic testing has gained in popularity around the world, including in the United States, and it is now becoming an integral aspect of genealogy.
There are many advantages to DNA testing, especially when it comes to genealogical research. A DNA test can not only help you learn more about your background, but it can also provide information about your potential health risks. DNA is used to determine kinship and it is a common tool applied in exhaustive genealogical research. Moreover, a DNA test can help resolve a variety of problems and build your family tree. The results of a DNA test can be used in different areas, such as:
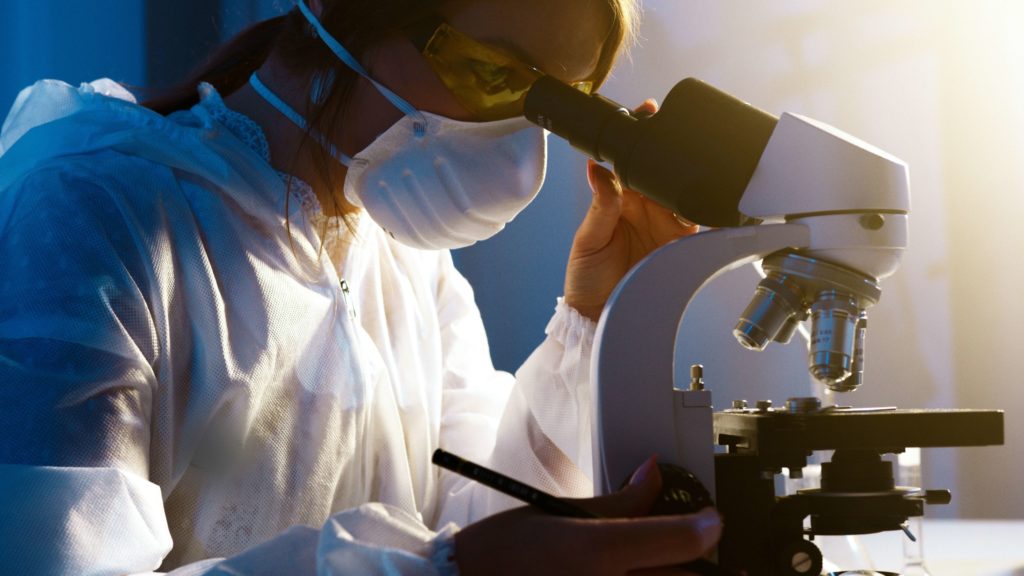

Many companies offer DNA testing and the average cost of tests ranges from about $50 to $700. Shipping costs depend on your country and the delivery agents you use.
Is one of the most important tools in a professional genealogist’s armoury. The most effective way of conducting genealogy research and finding sufficient evidence is to combine documentary search with a DNA test. Many companies in the USA that provide mtDNA, autosomal DNA and Y-DNA testing have an exhaustive matching database.
Can be useful in cases such as adoption, immigration, identifying legitimate ancestors, and confirming African or Native American ancestry. Even if we lack some historical records, DNA can help many African Americans or Jewish people discover their origins and family history.
Since your health is directly related to your genetics, а DNA test can also help identify potential health problems and predict many chronic illnesses, such as heart disease and cancer, or issues relating to fertility. The tests can reveal changes to your genes that may cause an illness so they are useful in terms of preventing future problems.
In genealogy research, there are three types of DNA test commonly offered:
Each test has its own characteristics and produces different information. To select the most appropriate test, it is important to clearly define your objectives and the desired outcome.
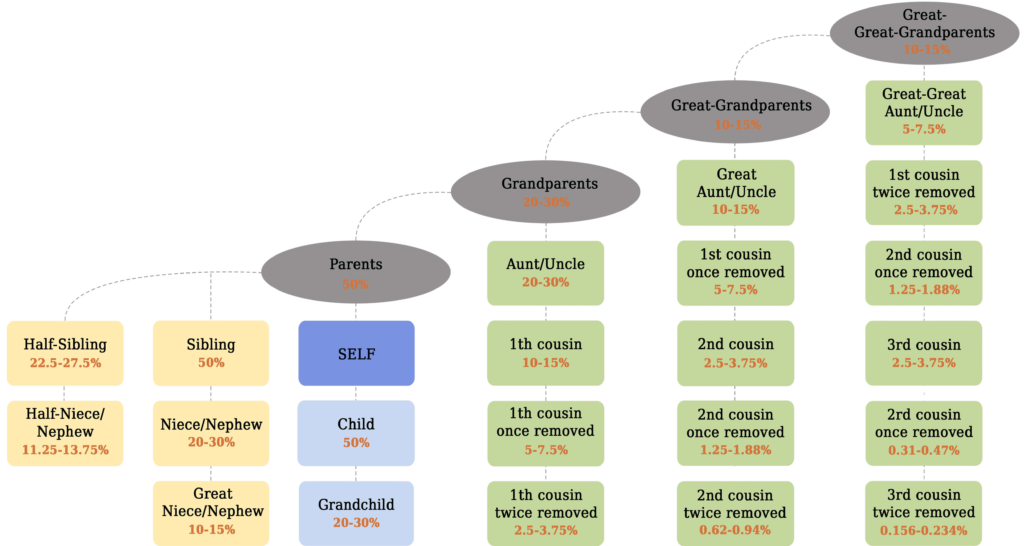
The most popular type is autosomal DNA testing. To date, more than 40 million people have tested their autosomal DNA. Besides the sex chromosomes (the X and the Y), the human cell nucleus contains twenty-two pairs of chromosomes that constitute the human autosomal DNA. Each individual inherits half of their autosomal DNA from their mother and half from their father. The percentage of autosomal DNA similarity depends on the level of the relationship. For example, siblings or parents and children share 50% of their DNA.
An autosomal test is ideal if you have questions about your family tree within 5–7 generations. Despite the widespread and accurate determination of kinship, autosomal DNA tests are not effective enough for issues concerning more distant generations.
Although X-DNA is less commonly used in genealogy, it does also contain information about your family tree. X-DNA is inherited by a child from their mother or passed from a father to a daughter. The difference is that X-DNA is almost never inherited by a son from a father.
The Y-chromosome is paternally inherited; women do not receive this chromosome. A special feature of the Y-chromosome is that it hardly changes from father to son. For this reason, we have the opportunity to reveal paternal ancestry using Y-DNA testing. Inheritance patterns of Y-DNA make it possible to carry out research into more distant generations.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a small genome found in the mitochondria and it is carried by both males and females. Mitochondrial DNA is passed almost unchanged from mother to child. Although males also receive mtDNA, they do not pass it on to their children. MtDNA is inherited through the direct maternal line. Consequently, mtDNA testing results can be used to study maternal ancestry.
Since Y-DNA and mtDNA do not alter a great deal from parents to children, Y-DNA and mtDNA tests provide information about the ancestral line for about 20 generations. However, information about specific ancestors is less accurate.
Although a DNA test can be incorrect, the advanced technology and large database usually prevent such errors from occurring. The main reasons why a DNA test may be incorrect include a:


As new data becomes available, your test results may also change slightly.
A DNA test cannot 100% guarantee your origin because it is impossible to directly compare your DNA to that of people who lived thousands of years ago. However, as more and more DNA tests are performed, so more detailed and accurate information is elicited. DNA testing companies have access to the genetic data of millions of people, making the tests more effective.
Genetic testing is used for a variety of reasons. Therefore, it is important to determine your goal in order to generate the most effective outcome. For this reason, it is recommended that you hire the services of a professional genealogist.
In order to obtain the desired outcome from the testing process, it is vital that the test results are correctly interpreted. To be most effective, genealogical tests should be supported by genealogy services.
In fact, I don’t make any profit from conducting DNA tests. My goal is to offer you another way of obtaining information that will advance the progress of your genealogical research. I will help explain the report, confirm or refute hypotheses, research your family tree or simply open up new opportunities for your search.
To get your free initial consultation and find out how I can help your particular case,

enquiry![]() truegenealogist.com
truegenealogist.com
